PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE,
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
SYLLABI OF M.A. SEMESTER SYSTEM
COURSES OF FIRST SEMESTER
Course Code |
Course |
CH |
Marks |
PS- 601 |
History of Freedom Movement 1857 to 1929 |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 602 |
Islam in South Asia “Part One” |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 603 |
Social System of Pakistan “Part One” |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 604 |
Geography of Pakistan “Part One” |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 605 |
Urdu (Optional) |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 606 |
Balochi (Optional) |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 607 |
Brahui (Optional) |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 608 |
Pashto (Optional) |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 609 |
English Compulsory |
2 CH |
50 |
Total CH |
26 CH |
|
|
COURSES OF SECOND SEMESTER
Course Code |
Course |
CH |
Marks |
PS- 610 |
History of Freedom Movement 1930 to 1947 |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 611 |
Islam in South Asia “Part Two” |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 612 |
Social System of Pakistan “Part Two” |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 613 |
Geography of Pakistan “Part Two” |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 614 |
Active Citizen |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 615 |
History of Balochistan “Part One” |
3 CH |
100 |
Total CH |
18 CH |
|
|
COURSES OF THIRD SEMESTER
Course Code |
Course |
CH |
Marks |
PS- 616 |
History of Balochistan “Part Two” |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 617 |
The Political and constitutional development in Pakistan 1947 to 1971 |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 618 |
Research Methodology |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 619 |
Economy of Pakistan “Part One” |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 620 |
Contemporary Issue of Pakistan |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 621 |
Basic Statistics “Part One” |
3 CH |
100 |
Total CH |
18 CH |
|
|
COURSES OF FOURTH SEMESTER
Course Code |
Course |
CH |
Marks |
PS- 622 |
The Political and Constitutional Development in Pakistan 1971 to 2013 |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 623 |
Economy of Pakistan “Part Two” |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 624 |
Foreign Policy of Pakistan |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 625 |
Disaster Management in Pakistan |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 626 |
Local Self Government in Pakistan |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 627 |
Basic Statistics “Part Two” |
3 CH |
100 |
PS- 628 |
Research Paper Writing and Presentation |
3 CH |
200 |
Total CH |
21 CH |
|
|
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
HISTORY OF FREEDOM MOVEMENT 1857 TO 1929
(COURSE CODE PS-601) CH 3
Introduction / Objective.
This course introduces students to the historical background of the creation of Pakistan. It focuses on major historical events both national and international and their impact, discuss and describe the contribution of religious institutions such as Deoband, Bravli and religious scholars in uprising of Indian Muslims, explore the political achievements of Ali Garh Movement and Sir Syed Ahmed Khan for Indian Muslims, look insight into the evolution of two nation theory and Lahore Resolution of 1940 and their contribution information of Pakistan.
FIRST SEMESTER
1. The Religion and Political Movement before 1857, with special reference to Shaikh Ahmed Sirhindi, Shah Wali Ullah, Jihad and Faraidi Movements.
2. The War of Independence 1857, its causes and effects.
2:1.Queen’s Proclamation- 1858,
2:2.The advent of the British Rule.
3. Sir Syed Shed Ahmed Khan and Aligarh Movement, educational and political achievements.
3:1.The Indian National Congress
3:2.The partition of Bengal
3:3.The foundation of All India Muslim League
3:4.Lucknow Pack.
4. The Balkan wars and their effect on the Muslims of the Sub-continent.
5. The Khilafat Movement and its effect on the Muslim Politics.
5:1.Nehru Report.
5:2. Jinnah Fourteen Points.
Basic Readings:
- Allana. G, Quaid-e-Azam, the story of a Nation Builders Lahore, 1967.
- Azad. A.K, India wins Freedom, Bombay, 1959.
- Aziz. A, Islamic Modernism in India and Pakistan (1858-1947), London, 1963.
- Aziz .A, Studies of Islamic Culture in the Indian Environment, Oxford, 1967.
- Graham. G.F.I, Lie and work of Sir Syed Ahmed Khan, London, 1871.
- Gopal. Ram, Indian Muslims: A Political History (1858-1947), Bombay, 1959.
- Hunter. W.W, Our Indian Muslims, London, 1871.
- Ikram. S.M, Modern Muslim India and Birth of Pakistan (1857-1951), Lahore, 1965.
- Nehru Jawaharlal, The Discovery of India, Delhi, 1985.
- Hector Bolitho, Jinnah, London, 1945.
- Tara Chand, History of Freedom Movement in India, 4 vol: N. Delhi, 1947.
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
ISLAM IN SOUTH ASIA
(COURSE CODE PS-602) PART ONE CH 03
Introduction / Objective.
This course introduces students to the tenants of Islamic faith, discuss and differentiate key political, social and economic concepts in light of Quran and Sunnah and western thoughts, describe the genesis of Islamic community at Madina, also trace the history of emergence of Islam in Balochistan.
FIRST SEMESTER
- Fundamental tenets of faith in the light of Quran and Sunah.
- Foundation of Islamic community at Madina and It’s expansion beyond the Arabian Penisula.
- Battle’s between Muslim and Non-Muslim, its causes and results.
- The early settlement of the Muslim communities in the Indo-Pak Sub-continent.
- Islam in Balochistan.
Books Recommended
- A.I.H. Qureshi Islamic thought and movement, Karachi, 1979.
- Tarachand, Influence of Islam of Indian Culture Lahore.
- Sohail Bhatii, Muslim rule in India & Pakistan
- Syed Ameer Ali, The Spirit of Islam.
- Khurshid Ahmed, Islam it’s meaning and message
- Abdullah Malik MA Tarekh-e-Islam
- Dr. Abdul Ali Tarekh-e-Islam or Islami Threke
- Prof. Khurshid Ahmed, Islami Nazariya Hayat
- Qadir Hussain Khan, South Indian Muslmans, Madrass 1910
- S.R. Sharma, The Religious Policy of Mughal Empire
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
SOCIAL SYSTEM OF PAKISTAN
(COURSE CODE PS-603) PART ONE CH 03
Introduction / Objective.
This course describe and discuss the social system and its definition & theories, to know the foundation of Muslim society, distinguish between west social system and Islam, analyze different cultures of Pakistani Society, differentiate and describe the similarities and dissimilarities among various cultures in Pakistan, explain the family structure and its function in Pakistan, know and explain social stratification social mobilize and social class.
FIRST SEMESTER
- INTRODUCTION.
Definition of Social System.
Theories of Social System.
Social System on Islam.
Basis of Muslim Society.
Islamic Social Order and national integration.
The family structures in Pakistan and its functions.
- CULTURE.
(A) |
Definition of Culture. |
|
The nature of Culture. |
|
Elements of national and regional culture. |
|
Islam and its impact on Social Life in Pakistan. |
(B) |
Analyzing Culture. |
|
A comprehensive study of Pakistani, cultures which includes Sindhi, Punjabi, Balochi, and Pashtoon and sub-cultures of Minorities having similarities and dissimilarities in Pakistan. |
BOOKS RECOMMENDED.
1. Samual Kooning, Sociology, an introduction to science of society, Barreness & Noble, London, 1968.
2. Iqbal Choudhry, Sociology, Aziz Publishers, Lahore, 1968.
3. Iqbal Choudhry, Pakistani society, Aziz Publishers, Lahore, 1991.
4. Abdul Hammed Taga. Sociology, in introduction, Amjad Book Dape Lahore, 1980.
5. Jan Mohammad, The Baloch Cultural hertiage, Royal Sindhi Culture.
6. Ansar Lahid, Sindhi Culture.
7. Tanveer Junejo, Immajiyt Ja Asul, Sindhology-sindho University Jamshoro, 1981.
8. Farukh Javaid, Umarniya-II.B.F.Karachi, (Urdu Books) 1979.
9. Dr. Syed Atta-u-Rahim, Ibitadai Umorniyat, 1983.
10. Ghulam Murtaza Shakir, Pakistan Koushra, I.K.Lahore, 1983.
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
GEOGRAPHY OF PAKISTAN
(COURSE CODE PS-604) PART ONE CH 03
FIRST SEMESTER
Introduction / Objectives
The aims and objectives of the course will be to acquaint the students with the Geography of Pakistan. After studying the course, a student should gain familiarity with the physical features, climate and environment of Pakistan. He or she will be able to understand such issues as population (both rural and urban) growth, features and characteristics of villages, towns and cities. Origin, distribution and special characteristics of these groups are to be studied and the common features of all groups are to be emphasized for finding unity in diversity. Another important aspect of the course will be the economy of Pakistan which includes under its rubric the agricultural areas of Pakistan, minerals, industrial development, trade and commerce, transport and communication.
Physical Geography
- Introduction; Brief History, location and geographical Importance
a. Introduction of Geography
b. Brief History of Pakistan
c. Location of Pakistan
d. Geographical Importance - Physiographic Features, General Relief
a. Mountains
b. Plateau
c. Plain
d. Deserts - Climate
a. Definition of climate
b. Temperature
c. Rainfall
d. Winds pressures
e. Climatic division of Pakistan - Natural vegetation and Rivers of Pakistan
a. Kinds of Natural vegetation in Pakistan
b. Indus River and tributaries - Soil and Minerals
a. Definition of soils
b. Kinds of soils in Pakistan
c. Kinds of Mineral, Basic and Non Basic Minerals
BOOKS RECOMMENDED.
- Johnson, B.L.E. Pakistan. London: Henman,1970.
- Kureishy, K.U.A. Geography of Pakistan. Karachi: Oxford University Press, 1978.
- Spate, O.H.K. India and Pakistan, A General Regional Geography. London, 1957.
- Khan, F.K. Geography of Pakistan, Environment People and Economy. Karachi: Oxford University Press, 1987.
- Khan, F.K. Pakistan: An Economic Geography. Karachi: Oxford University Press
- Khan, F,K. (1993). A geography of Pakistan: Environment, people, and economy. New York: OUP.
- Spate, O.H.K. and Learn Month, A.T.A., India and Pakistan: Land, People Economy. London, 1972.
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 50.
FUNCTIONAL ENGLISH
(COURSE CODE PS-609) CH 03
Course Objectives:
Being Lingua Franca of the world, the importance of English language cannot be denied. The command over written and spoken English is now considered to be a requisite for all the students. It prepares them with necessary skills and ability to deal successfully with the complex as well as challenging situations.
This subject certainly demands a systematic and comprehensive study of the related topics. The main objective of this course is to improve English language abilities of the students in a friendly atmosphere. To provide a sound base in the English grammar and composition.
To develop proficiency in the art of effective communication.
Course Contents:
First Semester;
GRAMMAR;
SENTENCE, BASIC KINDS OF SENTENCES, PRINCIPAL ELEMENTS OF SENTENCE, (SUBJECT, OBJECT, PREDICATE, HELPING VERBS, MODAL AUXILIARY VERBS, COMPLEMENT, EXTENTION OF PREDICATE), PART OF SPEECH, (NOUNS, PRONOUNS, ADJECTIVES, VERBS, ADVERBS, PREPOSITIONS, CONJUNCTIONS, INTERJECTIONS, ARTICLES), TRANSITIVE AND INTRANSITIVE VERBS, CAUSATIVE VERBSs, TENSES, ACTIVE AND PASSIVE VOICE, PHRASES AND CLAUSES, DIRECT AND INDIRECT SPEECH,
CORRECT USUAGE;
AGREEMENT OF THE VERB WITH SUBJECT. COMMON ERRORS USING NOUNS, PRONOUNS, CONJUNCTIONS. ERROR OF PROXIMITY, PAIR OF WORDS, PHRASAL VERBS, IDIOMS, VOCABULARY BUILDING, CONDITIONAL SENTENCES, GERUND AND PARTICIPLES, INFINITIVES, SEQUENCE OF TENSES.
STRUCTURES;
VERB PATTERNS, QUESTION TAGS, SHORT ANSWERS, MORE STRUCTURES.
WRITTEN COMPOSITION;
PRECISE WRITING, ESSAY WRITING, PARAGRAPH WRITING,
PUNCTUATION AND STYLE;
APOSTROPHE, BRACKETS, COLON, COMMA, DASH, EXCLAMATION POINT, HYPHEN, PARENTHESES, PERIOD, QUESTION MARK, QUOTATION MARK, SEMICOLON, SLASH.
Recommended BOOKS:
- Eastwood, J (2005) Oxford Practice Grammar. UK: Oxford.
- Martin & Wren (2007) High School, English Grammar & Composition. New Delhi: S Chand & Company Limited.
- Martinet & Thomson (1992) A practical English Grammar. UK: Oxford.
- Swan, M (2005) Practical English Usage. UK: Oxford University Press.
- Shah, Sayyid (2006) Exploring the world of English. Lahore: Ilmi Kitab Khana
Note: due to limited time certain skills will be given priority over others.
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
HISTORY OF FREEDOM MOVEMENT 1930 TO 1947
(COURSE CODE PS-610) CH 03
Introduction / Objective.
This course introduces students to the historical background of the creation of Pakistan. It focuses on major historical events both national and international and their impact, discuss and describe the contribution of religious institutions such as Deoband, Bravli and religious scholars in uprising of Indian Muslims, explore the political achievements of Ali Garh Movement and Sir Syed Ahmed Khan for Indian Muslims, look insight into the evolution of two nation theory and Lahore Resolution of 1940 and their contribution information of Pakistan.
SECOND SEMESTER:
1. Alama Iqbal’s Address at Allahabad, 1930.
1:1.Round Table Conferences.
2. The Constitutional Reforms and the enactment of Government of India Act 1935.
2:1.The separation of Sindh from Bombay presidency.
2:2.The Provincial Election (1936-37).
2:3. Congress Ministries.
3. The struggle for Pakistan: The Lahore Resolution of 1940.
3:1. Quit India Movement.
3:2. Cripps Mission.
3:3. Gandhi-Jinnah Talk.
3:4. Third June Plan.
4. The role of Baluchistan in the Freedom Movement.
5. The Quaid-e-Azam as an organizer of All India Muslim League and Mass Muslim Leader and Maker of Pakistan.
Basic Readings:
- Allana. G, Quaid-e-Azam, the story of a Nation Builders Lahore, 1967.
- Allana. G, Our Freedom Fighters, Karachi, 1969.
- Azad. A.K, India wins Freedom, Bombay, 1959.
- Aziz. A, Islamic Modernism in India and Pakistan (1858-1947), London, 1963.
- Gopal. Ram, Indian Muslims: A Political History (1858-1947), Bombay, 1959.
- Hunter. W.W, Our Indian Muslims, London, 1871.
- Nehru Jawaharlal, The Discovery of India, Delhi, 1985.
- Qureshi. I.H, Struggle for Pakistan, Karachi, 1965.
- Hector Bolitho, Jinnah, London, 1945.
- Tara Chand, History of Freedom Movement in India, 4 vol: N. Delhi, 1947.
- James, Raj: The Making and Unmaking of British India (2000).
- Rabbani. M. Ikram, A Comprehensive Book of Pakistan Studies, Edition. 3, Karachi, 2005.
- Aziz. K.K, The Making of Pakistan: A Study in Nationalism, London, 1967.
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
ISLAM IN SOUTH ASIA
(COURSE CODE PS-611) PART TWO CH 03
Introduction / Objective.
Through course students understand the role Sufis and Ulemas (religious scholars) in expansion of Islam and advancement of Muslim communities, describe the rights / duties of non-Muslim communities in an Islamic Rule and the rulers towards non-Muslims and impact of it on the relation between two communities, and also discuss the impact of Islamization on the economy, political system and society of Pakistan at large.
SECOND SEMESTER
- Geography of South Asia.
- The birth of Islam, Sea route, the Caliphate’s expedition’s to Sindh in the 8th Century.
- The role of Sufi’s and Ulemas in the Expansion of Muslim Community.
- Islam during the Ghaznavid, Gharid and Mughals.
- Islamization of Pakistani Society, Economy and Political system
Books Recommended
- M.A. Zafar A Short History of Pakistan 1985-2007.
- Pakistan the formation phase Oxford 1857-1948
- Richard Symonds The Making of Pakistan
- Ishtiaq Hussain The Struggle for Pakistan
- K.K. Aziz, The Making of Pakistan
- Dr. Hamidullah Shah Doghar’s Tarikh Pak-o-Hind Wafath Alamgir Se Wafath Zafar.
- Safar Imam, The Mulmans of the Sub-continent Lahore 1980.
- Abdul Kari, Special History of Muslims in Bangal, Dacca 1959
- A.I.H. Qureshi, The Muslim Community of the Indo-pak Sub-continent Karachi, 1977.
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
SOCIAL SYSTEM OF PAKISTAN “PART TWO”
(COURSE CODE PS-612) CH 03
Introduction/Objective.
To know and explain social stratification social mobilize and social class, identify and explain different factors responsible for social and culture change. Explain different aortal features of human biography with reference to population, agriculture transportation Industry and trade, describe geographical features of Balochistan including demography, soil and climate characteristics system of irrigation, communication system and mineral resources, recognize the potential and significance of coastal are in Balochistan.
SECOND SEMESTER |
|
- SOCIAL STRATIFICATION.
Social status and status ranking.
Social class and status grouping.
Social mobility.
The consequence of stratification.
- SOCIAL AND CULTURAL CHANGE IN PAKISTAN.
Meaning of Social change.
Different factors of social change.
Theories of Socio-cultural change.
Socio-Cultural changes in Pakistan Society.
Social Planning in Pakistan.
- SOCIAL PROSLEMS OF PAKISTAN WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO
BALOCHISTAN.
Population.
Education.
Health and Sanitation.
Agriculture.
Rural, Urban and Industrial.
Narcotics/Environment.
BOOKS RECOMMENDED.
1. Fahimita Masood,Moushrti Masail Ki Umarnityat, I.G.I, Karachi,1981.
2. Iqbal Choudhry,Umarsity, Aziz Publishers; Lahore, 1981.
3. Iqbal Choudhry,Pakistani Mouhashra, Aziz. Publishers, Lahore,1982
4. Shahid Hussain Farooq,Pakistani Musllamanonu Ki Rasam-o-Riwa Idera-Sakefat-e-Islamia, Lahore, 1981.
5. Pakistan Year Book, 1971 and onwards.
6. Muhammad Idris Siddiqui Wadia Sindhi-Tahzib (Urdu), Karachi, 1959.
7. Muhammad Idris Siddiqui, Dindkho Mather Ji Sabhita (Sindhi).
8. Murdock, George Peter. Social Structure the Free Press, New York.
9. Kuhn Alfred, The logic of social system, Jossey Boss Publishers San, Francisco, 1974.
10. Mohammad Khalid,A study of social work in Pakistan Kifayat Academy, Karachi, 1982.
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
GEOGRAPHY OF PAKISTAN “PART TWO”
(COURSE CODE PS-613) CH 03
SECOND SEMESTER:
Introduction/Objectives
The aims and objectives of the course will be to acquaint the students with the Geography of Pakistan. He or she will be able to understand such issues as population (both rural and urban) growth, features and characteristics of villages, towns and cities. Origin, distribution and special characteristics of these groups are to be studied and the common features of all groups are to be emphasized for finding unity in diversity. Another important aspect of the course will be the economy of Pakistan which includes under its rubric the agricultural areas of Pakistan, minerals, industrial development, trade and commerce, transport and communication.
Human Geography and a detailed study of Geography of Balochistan
- Population and Agriculture
a. Population
b. Density of Population
c. Urban and Rural
d. Agriculture’s Major crops - Industries and Trade
a. kind of industries in Pakistan
b. Trade of Pakistan - Physical Features of Balochistan
a. Mountains
b. Plateau
c. Plains - Development potential in the coastal area of Balochistan
a. Seaport
b. Fishing
c. Ship breaking - Minerals of Balochistan.
a. Basic and Non-Basic minerals
BOOKS RECOMMENDED.
- Johnson, B.L.E. Pakistan. London: Henman,1970.
- Kureishy, K.U.A. Geography of Pakistan. Karachi: Oxford University Press, 1978.
- Spate, O.H.K. India and Pakistan, A General Regional Geography. London, 1957.
- Khan, F.K. Geography of Pakistan, Environment People and Economy. Karachi: Oxford University Press, 1987.
- Khan, F.K. Pakistan: An Economic Geography. Karachi: Oxford University Press
- Khan, F,K. (1993). A geography of Pakistan: Environment, people, and economy. New York: OUP.
- Spate, O.H.K. and Learn Month, A.T.A., India and Pakistan: Land, People Economy. London, 1972.
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
ACTIVE CITIZENSHIP PROGRAM
(COURSE CODE PS-614) CH 03
SECOND SEMESTER:
Introduction/Objective.
The course seeks to educate the students about the concept of citizenship. The rights and responsibilities of citizens as member of local, national and global community and the modes of effective citizen participation in the uplift of society.
Active Plan for new Batch
S.# |
Module No. |
Activity |
1 |
Introduction |
Introductory Exercise (Globingo) |
|
|
Introduction of Active Citizen |
|
|
River Journey Set up |
2 |
Module I |
Me (Identity & Culture) |
|
|
1.1 My Identity |
|
|
1.2 Identity & Culture |
|
|
1.3 Bringing a Character to life |
|
|
1.4 How Identities Adapt |
3 |
Module II |
Inter Cultural Dialogue |
|
|
Example of dialogue using |
|
|
2.2. Debate & Dialogue |
|
|
2.4 Open Space-facilitating dialogue |
|
|
2.5 Learning about Dialogue: |
|
|
2.7. Creating dialogue through a world cate |
4 |
Thematic Module |
Gender Sensitization |
|
|
5.2 Switch Over |
5 |
Module III |
Local & Global Active Citizenship |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
Thematic Module |
Conflict Resolution |
|
|
6.1 What is conflict |
|
|
6.3 The Twister Game |
|
|
6.4 Red Flag |
|
|
6.5 The Anger volcano |
7 |
Module IV |
Project Planning & Delivery |
|
|
4.1 Introducing Planning : Tea making game |
|
|
4.2 Testing planning skills. “Lets Put on a Show” |
|
|
4.3 Project Planning & Need Assessments |
|
|
4.4. Benefits Assessments |
|
|
4.5. Our Ideas, Our Assumptions 109 |
|
|
4.7. Inform, Consult, Involve |
|
|
4.8 Influencing Skills. Advocacy & Diplomacy |
|
|
4.9 Dealing with people in Power |
8 |
Thematic Module |
Inclusive Development |
|
|
7.1 Feel to Learn |
|
|
7.2 Vocabulary Check |
|
|
7.3 An Enabled World |
Suggested Books.
- Lee, W. O. David L. Grossman, Kerry J. Kennedy & Gregory P. Fairbrother.(eds.) Citizenship Education in Asia and the Pacific: Concepts and Issues. Hong Kong: Comparative Education Research Centre, 2004.
- Crick, B. Education for Citizenship and the Teaching of Democracy in Schools, London: QCA, 1998.
- Dufour B & Breslin T. (eds) Developing Citizens. London: Taylor and Francis, 2005.
- Audigier, F. Basic Concepts and core competencies for education for democratic citizenship. Switzerland.: University of Geneva, 2000.
- Barbalet, J.M. Citizenship: Rights, Struggle and Class Inequality. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1988.
- Birzea, C. Education for democratic citizenship: a lifelong learning perspective. Strasbourg: Council of Europe.2000.
- Bottomore, T. Citizenship and Social Class, Forty Years on. Citizenship and Social Class. 1992.
- Clarke, J. Citizenship London: Pluto Press.1994.
- Davies, L. Citizenship Education and Human Rights Education: Key Concepts and Debates. London: British Council. 2000.
- Castells. The Information Age: Economy, Society and Culture. Oxford: Blackwell,1997.
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
HISTORY OF BALOCHISTAN “PART ONE”
(COURSE CODE PS-615) CH 03
Introduction/Objective.
After learning this subject the students will be easily understand the Muslim history in Balochistan, due to this subjects the students will understand the origin of Baloch Nationalism in this origin, The course subject is to create a good understanding among the students regarding the state of khan of Kalat and the emergence of dynastic rule.
SECOND SEMESTER:
- The land of Balochistan.
- Settlement in the area before Islam.
- Balochistan under the Muslim rule.
- Emergence of Dynastic rule.
BOOKS RECOMMENDED.
- Donce Longworth M, The Baloch Race. A Historical and ethnological Sketc, London, 1901.
- Hughes-Buller, R: Balochistan: Calcutta, 1908.
- Nasir Gul Khan Darjrh-e-Balochistan, (Two) Volumes), Quetta
1952/1954 (Urdu).
- Ram Hittu-tarikh-e-Balochistan; Quetta 1973.
(Firest Published in Urdu in 1904).
- Tuokar; a.L.P, Sir robert D, Sarrdeman, peaceful Congiseror.
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
HISTORY OF BALOCHISTAN “PART TWO”
(COURSE CODE PS-616) CH 03
Introduction / Objective.
After learning of this subject the student will comprehensively understand the arrival of British in Balochistan their policies towards Balochistan, students will able to describe the role of Balochistan in the freedom movement of Pakistan.
THIRD SEMESTER:
- The British influence in Balochistan their colonial Policies and interests.
- The Muslim rules of Kalat and their COLONIAL Policies and interests.
- Sangamon’s forward policy and British occupation of Balochistan.
BOOKS RECOMMENDED.
- Donce Longworth M, The Baloch Race. A Historical and ethnological Sketc, London, 1901.
- Hughes-Buller, R: Balochistan: Calcutta, 1908.
- Nasir Gul Khan Darjrh-e-Balochistan, (Two) Volumes), Quetta
1952/1954 (Urdu).
- Ram Hittu-tarikh-e-Balochistan; Quetta 1973.
(Firest Published in Urdu in 1904).
- Tuokar; a.L.P, Sir robert D, Sarrdeman, peaceful Congiseror.
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
THE POLITICAL AND CONSTITUTIONAL DEVELOPMENT IN PAKISTAN 1947 TO 971
(COURSE CODE PS-617) CH 03
Introduction / Objectives.
Pakistan has been facing constant political and constitutional crisis since birth. Parliamentary democracy is yet to be established on firms footing. This course has been designed with a purpose to appraise the students of nature and direction of constitutional and political development in Pakistan. After studying the course the students will be able to: § Understand the constitutional and political issues and problems of Pakistan § Comprehend the working of the political machinery and the adversities interposed in its way § Analyze the political problems of Pakistan
THIRD SEMESTER:
1. Interim constitutional arrangement.
2. The problems of Constitution Making 1947-1956.
3. The Constitution of Pakistan 1956, Salient features.
4. The Constitution of Pakistan 1962. Salient features.
5. Causes of failure of Constitution of Pakistan 1956, 1962.
6. The Constitution of Pakistan 1973. Salient features, And Amendments
in the Constitution 1973.
BOOKS RECOMMANDED
- Rizvi, Hasan Askari. Military and Politics in Pakistan 1947-199. Lahore: Sang-e-Meel Publication, 2000.
- Rizvi, Hasan Askari. Military, State and Society in Pakistan. Lahore, 2002.
- Feldman, Herbert. From Crisis to Crisis. London: Oxford University Press, 1972.
- Feldman, Herbert. Revolution in Pakistan. London: Oxford University Press, 1964.
- Sayeed, Khalid Bin. Politics in Pakistan: Nature and Direction of Change. np. nd.
- Sayeed, Khalid Bin. The Political System of Pakistan. Boston: Houghton Mifflin, 1967.
- Ziring, Lawrence. Pakistan in the 20th Century: A Political History. Karachi: Oxford University Press, 1997.
- Ziring, Lawrence. Pakistan: Enigma of Political Development. West View, 1980.
- Afzal, M. Rafique Political Parties in Pakistan. vol. I, II & III, Islamabad: National Commission on Historical and Cultural Research, 1999.
- Shafqat, Saeed. Political System of Pakistan and Public Policy. Lahore: Progressive Publisher, 1989.
- Burki, Shahid Javed. A Revisionist History of Pakistan. Lahore: Vanguard, 1998.
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
(COURSE CODE PS-618) CH 03
THIRD SEMESTER
Research Methodology (Compulsory)
Introduction / Objectives:
The purpose of this course is to Train the students in modern research techniques. Having gone through the course the students will be able to:
- Apply research techniques to Social Sciences
- Know the methodology of data collection and analysis
- Prepare research proposals.
Course Outline:
- Introduction
a. Definition, Importance and scope of research - Primary and Secondary sources.
- Types and Classification of Research
a. Basic Research
b. Applied Research
c. Action Research
d. Descriptive Method
e. Analytical Method. - Qualitative and quantitative research
- Objectivity and Subjectivity
- Hypothesis
a. Types and Characteristics of good hypothesis
b. Variable and its Types.
c. Literature Review - Sampling Technique
- Methods of Data collection
a. Interview
b. Questionnaire
c. Document Analysis - Preparing Research Proposal
- Documentation and Formatting.
Recommended Books:
- Goode, William J. Method in Social Research. New York: McGraw-Hill. Nd.
- C.R. Kotharic. Research Methodology; Method and Techniques. New Delhi: Wiley Eastern Ltd. 1993.
- F. Punch, Keith. Introduction to Social Research: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches. London: Sage Publication, 1998.
- Mikkelsen, Britha. Method for Development work and research: A Guide for Practitioners. New Delhi: Sage Publication, 1995.
- J.Goode Willaim & K. Hatt Paul. Method in Social Research. Singapore: McGraw-Hill, 1981.
- Kenneth S, Bordans. Research Design and Method. 5th edition, 2002.
- Kate. L. Turabaian. A Manual of Writers. Chicago: University of Chicago press 1973.
- Jahoda, Edutch, Etal Research Method in Social Relations
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
ECONOMY OF PAKISTAN “PART ONE”
(COURSE CODE PS-619) CH 03
Introduction / Objectives
Students will be able to:
· Understand key terms and concepts of economics · Identify the various economic institutions and their role in the growth of the economy of Pakistan · Identify the role of Agriculture & Industries in economic development of Pakistan · Identify the major economic issues and how they affect the economic development of Pakistan.
THIRD SEMESTER
- Introduction of Economics.
- Definition,
- subject matter
- scope.
- Factors of production.
Characteristics & Efficiency of
a). Land
b) Labour
c) Capital
d) Organizer
- Demand.
a) Definition of demand
b) Law of demand
c) Elasticity of demand - Supply
a) Definition of supply
b) Law of supply
c) Elasticity of supply - Population
a) Theories of population
b) Employment & unemployment problems
Books Recommended
- H. Gardezi and Jamil Rashid, Pakistan: The Unstable State. Lahore: Vanguard Books, 1983.
- Khan, Shahrukh Rafi. 50 Years of Pakistan's Economy: Traditional Topics and Contemporary Concerns. Karachi: Oxford University Press, 1999.
- Nabi, Ijaz. Agarian Economy of Pakistan: Issues and Policies. Karachi: Oxford University Press, 1986.
- Govt. of Pakistan, Annual Report 2002-2003: Review of Economy, State Bank of Pakistan. 2003.
- Haque, Irfan-Ul. Compendium of Pakistan Economy. Karachi: Royal Book Company, 1987.
- S M, Huda, Economic Development of Pakistan: From Self Reliance toDebt Ridden Economy. Karachi: Royal Book Company, 1996
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
CONTEMPORARY ISSUE OF PAKISTAN
(COURSE CODE PS-620) CH 03
Introduction / Objective.
The aim of the course is to examine the contemporary issues and problems in Pakistan in context of domestic and external environment. Describe the democratic process in Pakistan, know the issues related to globalization and its implication for Pakistan, have an understanding of new world order and discuss the role of Pakistan, understand the foreign policies of major powers / neighboring countries and in light of evaluate our Foreign policy with those countries.
THIRD SEMESTER:
Course Outline
1. Domestic Political Scenario: Challenges
2. Major Social, Cultural, Sectarian and Ethnic issues
3. Constitutional framework and Constitutional amendments
4. Pakistan’s Foreign Policy and the paradigm shift
a. Pakistan-US relations
b. Pakistan-India complexities
5. Pakistan’s Security in a Changing World
6. Education in Pakistan: Past Dilemmas and future prospects
7. Economic Challenges and Response
8. Futuristic Vision 38
a. Economic Prospects
b. External Relations
Books Recommended
- Arif, Working with Zia: Pakistan’s Power Politics 1973-1988, OUP, Karachi, 1995.
- Arif, Khaki Shadows: Pakistan 1947-1997, Karachi, 2001
- S.M. Burke, Pakistan’s Foreign Policy: An Historical Analysis, OUP, 1966.
- Shahid Javed Burki, Pakistan Under Bhutto, The Macmillan, 1980
- Keith Callard, Pakistan: A Political Study, 1957.
- Hamid Khan, Constitutional and Political History of Pakistan, Karachi, Oxford University Press, 2001.
- Ayesha Jalal, Democracy and Authoritarianism in South Asia, Sang-eMeel, 1995.
- Charles Kennedy (Ed.), Pakistan 2005, Karachi, Oxford University Press, 2006.
- Tariq Rehman, Denizens of Alien Worlds: A Study of Education, Inequality and Polarization in Pakistan, Karachi, Oxford University Press, 2004.
- Hasan Askari Rizvi, The Military and Politics in Pakistan, Lahore, 1974
- Lawrence Ziring, Pakistan in the Twentieth Century, OUP, 1997.
- Akbar Zaid, Political Economy.
- Farooq Mahmood, Ethnicity in Pakistan.
- Akbar S. Ahmed, Jinnah, Pakistan and Islamic Identity: The Search for Saladin, Karachi, 1997.
- Naseem S.M., Pakistan’s Economy, Karachi, Oxford University Press
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
BASIC STATISTICS “PART ONE”
(COURSE CODE PS-621) CH 03
Introduction / Objective:
Meaning and definition of statistics, relationship of statistics with social science, characteristics of statistics,. Frequency distribution: Organization of data, array, ungrouped and grouped data, types of frequency series, individual, discrete and continuous series, tally sheet method, graphic presentation of the frequency distribution, bar frequency diagram histogram, frequency polygon, cumulative frequency curve.
THIRD SEMESTER
- Function of statistics , Importance of Statistics in Research , Frequency Distribution , Measure of Central Tendency ( Sample and group data ) , Measure of Dispersion ( Sample and group data )
- Definition : Sample , Random Sampling , Stratified Sampling , Systematic Sampling , Cluster Sampling
- Hypothesis Testing , Type I and Type II error
Testing Hypothesis about Mean; Tests based on Normal Distribution (Z-test)
Test Based on t-distribution (Paired and Unpaired)
BOOKS RECOMMENDED:
- Introduction to Statistics Theory Sixth edition (part I and part II) by Sher Muhammad Chaudhry 6th edition.
- Principles and Procedure of Statistics: A Biometrical Approach by Robert G Steel , James H Torrie, David A Dickey 3rd edition .
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
THE POLITICAL AND CONSTITUTIONAL DEVELOPMENT IN PAKISTAN 1971 TO 2013
(COURSE CODE PS-622) CH 03
Introduction / Objectives.
Pakistan has been facing constant political and constitutional crisis since birth. Parliamentary democracy is yet to be established on firms footing. This course has been designed with a purpose to appraise the students of nature and direction of constitutional and political development in Pakistan. After studying the course the students will be able to: § Understand the constitutional and political issues and problems of Pakistan § Comprehend the working of the political machinery and the adversities interposed in its way § Analyze the political problems of Pakistan.
FOURTH SEMESTER:
- Early Problems of Pakistan.
- Political instability in Pakistan ,Causes and Impact.
- Democracy in Pakistan.
- Role of Political Parties in Pakistan.
- Role of Military in Politics.
- Role of Bureaucracy in Pakistan.
- Islamization in Pakistan.
BOOKS RECOMMANDED
- Burki, Shahid Javed, A Revisionist History of Pakistan. Lahore: Vanguard, 1998.
- Shafqat, Saeed. Political System of Pakistan and Public Policy, Lahore: Progressive Publisher, 1989.
- Rizvi, Hasan Askari, Military and Politics in Pakistan 1947-1997. Lahore: Sang-e-Meel Publication, 2000.
- Ziring, Lawrence. Pakistan: An Enigma of Political Development. Folkestone, Kent: Dawson; Boulder, Colo.: Westview, 1980.
- Jalal, Ayesha. Democracy and Authoritarianism in South Asia: A Comparative and Historical Perspective. Lahore: Sang-e-Meel Publications, 1995.
- Sayeed, Khalid Bin. The Political System of Pakistan. Boston: Houghton Mifflin, 1967. 42
- Bose, Sagata. and Ayesha Jalal. Modern South Asia; History, Culture, Political Economy, New Delhi: 2004.
- Rizvi, Hasan Askari. Military State and Society in Pakistan. Lahore: 2002.
- Waseem, Muhammad. Politics and State in Pakistan, Islamabad.
- Afzal, M. Rafique. Political Parties in Pakistan. vol. III, Islamabad: NIHER, 1999.
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
ECONOMY OF PAKISTAN “PART TWO”
(COURSE CODE PS-623) CH 03
Introduction / Objective
Students will be able to:
· Understand key terms and concepts of economics · Identify the various economic institutions and their role in the growth of the economy of Pakistan · Identify the role of Agriculture & Industries in economic development of Pakistan · Identify the major economic issues and how they affect the economic development of Pakistan.
FOURTH SEMESTER
- Agriculture
a. Over all agricultural situation of the country
b. Major crops
c. Source of irrigation
d. Relationship of agricultural with industries
e. Agricultural marketing
f. Land reforms
g. Problems & remedies - Industries
a. Back ground of industrial development
b. Role of industries in economic development
c. Large, small & light industries - Foreign Trade
a. Balance of trade
b. Term of trade
c. Balance of payment
d. Main import & export of Pakistan - Planning and Economic Development
a. Objectives, strategies, priorities & size of plans
b. Definition and concept of economic development
c. Characteristics of developing countries - Natural Resources
Its influence on the economy of Pakistan and on the Global world.
Books Recommended
- Saeed Khawaja, Amjad. Economy of Pakistan 2000-2001. Karachi: Institute of Business Management , 2001
- Uzair, Mohammad. Economy of Pakistan: Perspective and Problems. Lahore: Royal book Company, 2004.
- Ahmad, Khurshid. Elimination of Riba from the Economy. Islamabad: Institute of Policy Studies, 1995.
- William E, James. Foundations of Pakistan Political Economy: Towards an Agenda for the 1990s. Karachi: Oxford University Press, 1992.
- Akbar Zaidi, S, Issues in Pakistan's Economy. Karachi: Oxford University Press, 1999.
- Govt of Pakistan, Leading Issues Facing Pakistan Economy, State Bank of Pakistan. 2003.
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
FOREIGN POLICY OF PAKISTAN
(COURSE CODE PS-624) CH 03
Introduction / Objective:
This course is designed to familiarize the students with the basic principles and objectives of the foreign policy of Pakistan. The course covers the different conduct of Pakistan foreign policy from 1947 to to-date. Moreover, major issues rising from changing political realities have also been given due weight.
FOURTH SEMESTER
Chapter-I THE MAKING OF FOREIGN POLICY.
Brief description of the theoretical concepts of Foreign Policy of Pakistan.
Chapter-II. The Factors which influence foreign Policy.
- i) Bureaucracy (ii) Military (iii) Business elites.
iv) Political Prodesses: Political Parties, Parliament,
Press and Public Opinion.
- The Religious Elites Pressure Group.
- Multinational Corporations.
- Foreign Powers and Foreign Aid.
Chapter-III. Approaches to the Study of Foreign Policy.
- Traditional approaches.
- Modern approaches.
- System & analysis.
- Decision making approach.
- National Power Approaches.
- Quantitative approaches.
Chapter-IV. Pakistan and the Regional Powers.
- Pakistan’s relations with India.
- Pakistan’s Relations with China.
- Pakistan’s relations with Afghanistan.
- Pakistan relations with Iran.
Note:- All the theoretical concepts are to be taught with special reference to Pakistan Policy.
Chapter. V. Pakistan and the super powers.
Chapter.VI. Pakistan and Europe (West an Socialist East.)
Chapter.VII. Pakistan and the Muslim World.
Chapter.VIII. Pakistan and the Third world countries and National liberation-
Movement.
Chapter-IX. Pakistani International/Regional Organization.
i). Pakistan and the UN. ii) Pakistan and the O.I.C.
iii). Pakistan and the R.C.D. iv). Pakistan and the EEC.
v). Pakistan and the NAM. vi). Pakistan and the SAARC.
BOOKS RECOMMENDED.
- Ahmad, Javeed (ed). Pakistan’s Political, Economic and Diplomatic Dynamics. Lahore: Studio 4, 1999.
- Ahmar, Moonis (ed). Internal and External Dynamics of South Asian Security, Karachi,1998.
- Hasnat, Syed Farooq and Pelinka (ed). Security for the Weak Nations. Lahore: Izharsons, 1986.
- Hussain, Arif. Pakistan: Its Ideology and Foreign Policy. London: Frank Cass, 1966.
- Hussain, Irtiza. Strategic dimensions of Pakistan’s Foreign Policy. Lahore: Progressive Publishers, 1989.
- Malik, Hafeez. Soviet-American Relations with Pakistan, Iran and Afghanistan. London: Macmillan, 1994.
- Palmer, Norman D. South Asia and United States Policy. N.Y: Houghton Mifflin, 1996.
- Qureshi, Ejaz Aslam (ed.). Pakistan and South Asian Environment. Lahore: Sang-e-Meel Publishing, 1991. 28
- Shelton, U. Kodikara (ed.). External Compulsions of South Asian Politics. Karachi: Oxford University Press, 1993.
- Yunus, Mohammad. Foreign Policy: A Theoretical Introduction. Karachi: Oxford University Press, 2003.
- Wirsing, R.G. Pakistan’s security under Zia. London: McMillan. 1991
- Burke, S.M. Pakistan’s foreign policy. Karachi: OUP. 1990.
- Rizvi, Hasan Askari. Pakistan and the Geo-strategic Environment: A study of Foreign Policy. St. Martin’s Press, 2000.
- Shahid, M. Imtiaz (ed), Contemporary Affairs. Lahore: Caravan Enterprises, 2001.
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
DISASTER MANAGEMENT IN PAKISTAN
(COURSE CODE PS-625) CH 03
FOURTH SEMESTER
Natural Disasters and their Management in Pakistan
Introduction / Objectives:
The purpose of this course is to impart knowledge regarding causes and effects of various natural disasters, like floods, earthquakes and landslides and the key strategies for their management.
Course Outline:
1. Disasters and Disaster Management
a. Definition
b. Key concepts
c. Importance of the issue.
2. Major Natural Disasters in Pakistan: Their Causes, intensity and
Distribution
a. Floods
b. Earthquakes
c. Landslides and Snow Avalanches
d. Coastal Flooding
3. Effects of Disasters
a. Visible losses
b. invisible losses
4. Disaster and Social Issues
a. Nature of the problems faced by the victims
b. Loss of life and property (moveable and immovable)
c. Psychological problems
d. Gender issues
e. Child trafficking
5. Major Problems in Disaster Management
a. Problem of forecasting and dissemination of information
b. Lack of coordination among disaster management organizations
c. Shortage of trained human resources
d. Unavailability of advanced technology
e. Lack of planning.
6. Different Techniques in Disaster Management
a. Hazard assessment
b. Risk perception versus risk assessment
c. Risk management
i. Land use planning
ii. Forecast
7. Preparedness and Mitigation.
a. Disaster capacity building
b. Coordination among disaster management organizations
c. Organization of volunteers
d. National policy making
i. Re-construction activity relief
ii. Rehabilitation activity
e. Institutional mechanism (NADMA, PDMA, DDMA)
i. National Disaster Management Authority
ii. Provincial Disaster Management Authority
iii. District Disaster Management Authority
Recommended Books:
- Scholr, C.H. The Mechanics of Earthquake and Faulting. New York: Cambridge University Press, 1990.
- Bolt, B.A. Earthquakes. New York: W.H Freeman and Co, 1993.
- Birkeland, P.W, Soils and Geomorphology. New York: Oxford University Press, 1984.
- Lomnitz, C. Fundamentals of Earthquake prediction New York. J. witey & Sons, 1994.
- Reiter, L. Earthquake Hazard analysis – Issues and Insight. New York: Columbia University Press, 1990.
- Ward, S.N. A Multidisciplinary approach to seismic hazard in south California Seismical society . Bulketin 1994.
- Fowler, C.M.R. The solid earth an introduction of global geophysics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1990.
- Nakata, T, Tsutsumi, H. Khan, S.H, and Lawrence R.D. Active faults of Pakistan: Map sheets and inventories. Hiroshima: Research Center for Regional Geography, 1991.
- Davision, C. The Founders of Seismology. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1927.
- Hass, J.E., and D.S. Mileti. Socioeconomic Impact of Earthquake Prediction on Government, Business and Community. Boulder: Institute of Behavioral Sciences, University of Colorado, 1976.
- Yeats, R.S Living with Earthquakes in California A Survivor’s Guide. Gorvallis: Oregon state University Press, 20
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
LOCAL SELF-GOVERNEMNT IN PAKISTAN
(COURSE CODE PS-626) CH 03
FOURTH SEMESTER
Introduction / Objectives:
The course is designed to acquaint students with concept of local self-government, its institutions, functions and significance in Pakistan. It will also facilitate it’s in assessment of the performance of local government and suggesting warp to improve its functioning.
Course Outline:
1. Local government
a) Meaning
b) Scope
c) Need for local government.
d) Scope of local government
2. Organizational Structure of local government in Pakistan
a) Structure of local government
b) Relationship with provincial and central government and
implications on the performance of local government
c) Key functions of districts.
3. Functions of local government in Pakistan'
a) Key functions of union council
b) Key functions of tehsil
c) Key functions of districts.
4. Planning, development, budgeting and financial autonomy in
local government.
5. The role of local government in national development
6. Problems of local government in Pakistan.
7. The role of citizens in local self-government.
8. A brief comparative study of local government system
In Pakistan, and a SAARC country.
9. Restructuring of local government: Devolution Plan 2000; vision, principles, the structure of District government.
Recommended Books:
- Quddus, Abdul, Local self-Government in Pakistan. Lahore: Vanguard Books Ltd, 1981.
- Muhammad Asif Malik, Local Self Government in Pakistan. Iftikhar Ahmed Publisher, 2006.
- Sproats, Kevin. Local Government in Asia and the Pacific: A comparative analysis of fifteen countries. Sydney: Western Sydney Research Institute, nd.
- Government of Pakistan. Devolution Plan 2000. Islamabad: National Reconstruction Bureau, 2000.
- M.A. Muttalib and Muhammad Akbar Ali Khan, theory of Local Government, New Delhi, Sterling Publishers, 1983.
- Masudul Hasan, History of Local Government in Pakistan, Islamabad, Ministry of Local Government and Rural Development, 1984.
- Government of the Punjab, (2001) Local Governments Ordinance, Lahore: Govt. Publication.
- Hasan, Masudul. (1986) Text Book of Basic Democracy & Local Government in Pakistan, Lahore: All Pakistan Legal Decisions.
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
BASIC STATISTICS “PART TWO”
(COURSE CODE PS-627) CH 03
Introduction / Objective:
Meaning and definition of statistics, relationship of statistics with social science, characteristics of statistics. Frequency distribution: Organization of data, array, ungrouped and grouped data, types of frequency series, individual, discrete and continuous series, tally sheet method, graphic presentation of the frequency distribution, bar frequency diagram histogram, frequency polygon, cumulative frequency curve
FOURTH SEMESTER
- Concept of Experiment Design, Planning of Experiment, Basic principal of Experiment Design, Analysis of Variance ( ANOVA ) one way ANOVA with equal and unequal sample size, Two way ANOVA, inference about Mean after ANOVA, Multiple comparison Tests (LSD and DMR).
- Layout and Analysis of Completely Randomized Block Design, Advantages and Disadvantages of CRD and RCBD, Construction and Layout of Latin Square Design
- Factor Experiments advantage and disadvantages. F n series factorial (2
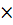 2) experiment.
2) experiment.
BOOKS RECOMMENDED:
- Introduction to Statistics Theory Sixth edition (part I and part II) by Sher Muhammad Chaudhry 6th edition.
- Principles and Procedure of Statistics: A Biometrical Approach by Robert G Steel , James H Torrie, David A Dickey 3rd edition .
PAKISTAN STUDY CENTRE
UNIVERSITY OF BALOCHISTAN, QUETTA.
Marks. 100.
RESEARCH PAPER WRITING AND PRESENTATION
(COURSE CODE PS-628) CH 03
FOURTH SEMESTER
RESEARCH PAPER WRITING & PRESENTATION.
(Technical Writing and Presentation Skills)
Objectives: Enhance language skills and develop critical thinking
Course Contents
Academic writing
How to write a proposal for research paper / term paper
How to write a research paper / term paper (emphasis on style, content, language, form, clarity, consistency)
Presentation skills
Recommended books:
Technical Writing and Presentation Skills
a) Presentation Skills
b) Reading
The Mercury Reader. A Custom Publication. Compiled by norther Illinois University. General Editors: Janice Neulib; Kathleen Shine Cain; Stephen Ruffus and Maurice Scharton. (A reader which will give students exposure to the best of twentieth century literature, without taxing the taste of engineering students).
(Compulsory for all students).